We live in a digital world that is becoming a bit more connected with each passing day. This connected world is increasingly driven by data thanks to AI, machine learning and data science.
As a data analyst, you have your finger on the pulse of the times and can positively influence economic and social developments through a good analytical understanding. It is a job that entails a lot of responsibility. Because where you work with data, you also have to act with great caution.
Therefore, it is not surprising that numerous well-known companies are looking for good data analyst candidates. We show you how you can become a data analyst as a career changer, what you need to do so, and what exciting opportunities this profession, which is considered the hottest job of the decade, offers you on a daily basis.
And best of all: thanks to Education voucher you can even get further training free of charge under certain conditions.
What is data analysis and why is it so important?
Data analysis is a process of gaining insights from unorganized information (data). Data can take many, different forms. For example, vacation pictures and voice files are just as much data as a first name and a phone number. By systematically examining this data for patterns and relationships to one another, data analysts seek to draw useful insights from it and communicate them to others in an understandable way.
The work of a data analyst begins with so-called raw data. Raw data is initially unordered. As long as they are not cleaned up first, the data analyst cannot derive any insights from them. In other words, order must first be brought into the chaos in order to make data usable. That is the job of a data analyst.
Collecting, cleaning and organizing data is a major part of data analysis. To do this, data analysts use various methods from statistics, programming and visualization. However, data analysts don't have to be one hundred percent proficient in these disciplines, because many of these steps have now been automated and run partly on their own. You just need to understand these processes well in order to manage them and control the results.
Data analysis is important for two reasons. First, it facilitates decision making, and second, it makes decisions provable based on facts. That's what makes it so valuable for companies that need to incorporate many, diverse data to strategically align themselves wisely.
So instead of just relying on your gut feeling, as a data analyst you make decisions based on facts. Even if data analysis is not always 100 percent correct, it is the best tool for predicting trends and developments.
In practice, it can indicate future sales figures and helps with product development and sales strategy. However, it does not have to be used only in the economic sense. There are also data analyses in the health sector, agriculture or in the government apparatus.
The tasks of a Data Analyst
Put simply, a data analyst collects and prepares a large amount of data and then performs analysis on those data sets. As a Data Analyst, you look for ways to harness data to gain insights, answer questions, and solve problems. The analyses a Data Analyst creates should lead to better, more informed business decisions.
With the results, a company can reduce manufacturing costs, increase customer satisfaction, or solve other problems that cost a company money. The data analyst works as part of a team with data scientists and data engineers.
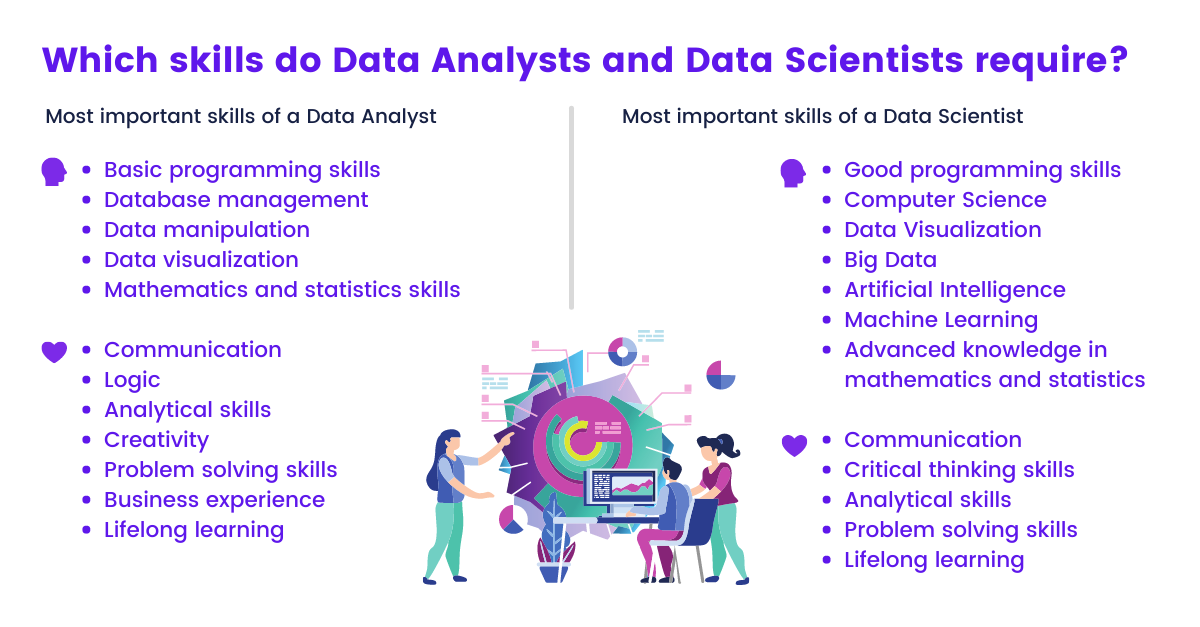
What is the difference between Data Analyst and Data Scientist?
Often, the distinction between the two job roles is blurred because the professional field surrounding data science is still relatively young and continuously evolving. The Data Scientist differs from the Data Analyst primarily in their advanced job skills.
Both roles share many, similar tasks, are equally qualified to analyze and interpret data, but in addition, the Data Scientist has in-depth knowledge of programming and mathematical modeling. This allows the Data Scientist to tackle deep problems, such as automating processes and programming artificial intelligence.
The Data Analyst takes on the role of a contractor and supervises tasks defined by other departments. The Data Scientist, on the other hand, searches independently for opportunities for improvement. While a bachelor's degree is sufficient to start as a data analyst, a master's degree is often required for a data scientist.
Your tasks as a Data Analyst
1 Formulate question
Your analysis starts with the definition of what you want to find out. The results of a data analysis are only as good as the question with which the analysis was started. To formulate the right question, you need to define the goal of the analysis. In a way, it is the most important part of the analysis process.
The crux is that quite often, the obvious problem, does not lead to the core of the solution. Even Albert Einstein said, "You can never solve problems with the same mindset that created them." So it is important to first look at a problem from different perspectives and to have a basic understanding of the needs and requirements of an organization.
2 Collect data
Once you have identified the right question, you need to determine what data you need to answer it. Two scientific approaches help you here: quantitative and qualitative analysis. Quantitative analysis is about large amounts of data, while qualitative analysis is about getting the most meaningful feedback possible, such as customer reviews. To do this, data analysts use three different data sources:
- First-party datathat are collected directly from you or your company
- Second-party datathat come from another company
- Third-party datathat come from other sources such as social media
To collect second- and third-party data, you need to think about a good strategy and use data from surveys, observations from social media posts, or online tracking from a website. Once you have collected enough data, it needs to be cleaned.
3 Clean data
The raw data that you have now are not yet sorted, have not been brought into a uniform format or are partially incomplete. To prepare them for data analysis, you must first bring them into a uniform state. First you look for errors, duplications, outliers and placeholders and eliminate them. Then you check again whether the data now meets your requirements or whether you need to review it again. Data analysts also refer to this procedure as data wrangling.
4 Analyze data
Once you have cleaned your data set, it is ready for analysis. Here, data analysts have several options at their disposal and you have to decide which approach is best suited for the respective question:
- The descriptive analysis summarizes characteristics of a data set and attempts to describe them. While it does not allow for definite conclusions, it is very useful in determining which next analysis steps are appropriate.
- The diagnostic analysis is designed to understand causes and relationships. Examining the relationship of two values, can help identify problems. This step also helps to review your own question and adjust it if necessary.
- The predictive analysis helps to read trends and developments based on past data.
- The prescriptive analysis can be useful in deciding how to proceed and is also used as a machine learning technique when computers are to learn to make predictions on their own.
5 Visualize and communicate data
After you have applied the analysis techniques to the data, there is one last important step. You still need to communicate the results of your analysis and explain them in an understandable way to others who don't have the same or even any analysis skills. To do this, you visualize the data and create appropriate charts, graphs, presentations, reports or interactive dashboards that visually support your findings.
This step is very important and has the goal that everyone can immediately interpret the results correctly at a glance and understand them themselves so that they can put them into their own words. If the visualization is simple and unambiguous, it is of high value for further decision making.
Become a data analyst: These 9 skills you really need
A career in data analytics can require a wide variety of skills, including technical and non-technical. This also includes the specific application of tools. Which skills are needed depends entirely on the company, the industry, and the exact role. With that said, let's take a look at the most important and most common nine skills that are important for your start as a data analyst.
Become a data analyst: Technical skills
1 Programming knowledge
Most of the time, a job as a data analyst requires, above all, the collection, preparation and analysis of data. In addition, programming skills are an advantage in order to be more flexible and independent of analysis software. This can save time in the day-to-day job. Python skills in particular are in high demand. Because of all the programming languages that exist, Python is the preferred one. If you don't have any previous knowledge, that's not a big deal. Even as a complete beginner, Python skills can be learned relatively easily with an in-service training.
2 Databases and their languages
The Data management requires understanding the particular language of a database. A database comes into play where the capacity of Excel ends. It is a system where very large amounts of data are stored and retrieved. A data analyst must be able to recognize the structures of databases in order to gather the information needed for analysis.
3 Data manipulation
In very few cases is the data ready for analysis from the start. As already mentioned at the beginning, data are often incomplete, not sorted or are available in different formats. Data sets must therefore first be cleaned. Analysts often use a language such as Python to prepare data for analysis. This process is called data manipulation.
4 Data visualization tools
What does a data analyst do with the results of their analysis? Data visualization is a powerful capability for communicating results. Tools like Matplotlib, JavaScript d3.js, and Tableau help with this. Mastering these tools is important, but even more important is understanding the principles of how to successfully visualize data and communicate it in an understandable way using data storytelling.
5 Mathematics and statistics
Statistics and linear algebra are skills that a data analyst should have or learn. They are crucial when it comes to performing tests and, in very advanced cases, also necessary to decide how algorithms can be optimized. For the second case, programming knowledge in Python often already offers great assistance.
Become a data analyst: Non-technical skills
6 Logic
A bright mind will get you far. A useful skill for data analysts is to use logical thinking patterns that do not require higher mathematics. Often, a data analyst must be able to think well within the context of his or her analyses in order to set interesting questions and critically examine the results. Data analysis is a broad field with a variety of tasks.
Depending on the task, special knowledge is needed. It is important to have a basic understanding of mathematics and statistics, but it is even more important to be able to look at problems in an analytical way. 80 percent of a data analyst's work consists of preparing, sorting, and visualizing data, which usually does not require higher mathematics.
7 Creativity
Data storytelling and presentations go hand in hand. But good presentation skills don't come naturally. The ability to tell a compelling story with data is critical to properly convey insights and engage audiences. It's an art in itself to express complex relationships simply without distorting the content. For this reason, data visualization and good data storytelling are important skills for a data analyst to master.
8 Social skills
It is important to understand who the customer of an analysis assignment or the target group of a presentation is and what prior knowledge these people have. This is especially true if the insights cannot be recognized easily and quickly. Often, other departments lack the knowledge to properly interpret the results of a data analysis. A data analyst knows what information his audience needs and how best to convey it.
9 Business experience
Understanding what a company's goals are is critical when it comes to making informed, data-driven decisions. Data Analysts should not only understand how data can impact their company's decisions, but they should also know how to interact with engineers or product managers, for example, or have industry knowledge. Both a technical and non-technical understanding of the business and its internals is essential for the data analyst job.

What tools and programming languages do data analysts use?
Microsoft Excel
As a conventional data analysis tool, Microsoft Excel offers a wide range of functions. These range from sorting and editing data to displaying this data in the form of charts. A good understanding of Microsoft Excel is very helpful for the job as a Data Analyst.
SQL
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a programming and database language and is used for database management.
Python
Python is a very common and almost indispensable programming language for data experts. Fortunately, it is easy to learn and understand. Plus, it's open source, which means you can customize and develop it on your own.
SAS
SAS has been developed by SAS Institute for functions such as advanced analytics, building predictive models, business intelligence and data management. It is very useful because it can easily handle any type of statistical modeling of large amounts of data.
R
An alternative to SAS is R, a programming language and software environment for statistical computing and graphing. The advantage of R is that, as free open source software, it invites you to customize it for your own purposes.
At first, learning these tools and languages may sound difficult and you may not know where to start. We can take away that worry. As with any new skill you learn, it's all about starting small. Whether you're learning to cook, play an instrument or paint, you always start with the basics. And these can even be learned on the side, if you keep at it. In the end, what counts is: Practice makes perfect.
How can I become a data analyst? Career change, retraining & co.
Your career as a Data Analyst starts with learning job-relevant skills. As a newcomer with no math or programming background, this means first and foremost familiarizing yourself with basic skills and understanding the analysis process. Once you've gathered the most important skills, you can start thinking about applying for a job as a data analyst.
Even if this process sounds effortless, such a career change requires a lot of personal commitment. To learn everything you need for this change and to draw on the expertise of experienced data experts, it is worth considering online courses for your retraining as a data analyst.
Upon successful completion, such a course can mean certification as a data analyst, which is an important alternative to the classic university degree. To take the first step on your new career path, you can find out about course offerings and funding opportunities through the Federal Employment Agency or the Job Center at StackFuel.
Everyday work as a data analyst: real-life example
The day-to-day work of Data Analysts depends entirely on the industry or company. They may be responsible for creating dashboards, maintaining databases, and performing analyses for various departments in the company. Most of them work closely with IT teams, management, business departments and Data Scientists.
Depending on the task, the knowledge and tools a data analyst works with vary. Some Data Analysts don't even use programming languages and work mainly with statistical software and Excel. Because the field of data analysis is so diverse, a Data Analyst may spend the morning, for example, cleaning data and the afternoon creating concrete, customized solutions. Let's try to outline a possible day in the life of a Data Analyst.
In the morning, Data Analyst Lisa uses SQL to retrieve data from a database and then analyze it. To do this, she works in a table with customer data such as name, age, postal code and value of goods. Lisa wants to find out where customers shop most frequently, but there are many data gaps in the table, so she discusses with her manager how to deal with the gaps. The manager decides that she needs to coordinate with different groups of people or stakeholders.
She must discuss with IT how the data gaps arose so that they can be eliminated afterwards. With her contact from the business department that commissioned the analysis, she needs to agree on how to deal with the data gaps. They decide to use artificial intelligence and machine learning to fill in the gaps. To do this, Lisa continues to work with an expert on her team.
Later that day, Lisa works on visualizing the results of her latest analysis and turning them into a presentation to present to her team in order to jointly determine the next steps. In doing so, Lisa places particular emphasis on ensuring that the presentation of the results is coherent and easy to understand in order to simplify a decision.
The many job opportunities of the Data Analyst
An indispensable basis is, of course, that a company operates digitally. The more digitally oriented the company, the more data it has at its disposal. Classically, data experts are therefore urgently sought especially in the finance, insurance, online retail, energy, telecommunications and healthcare sectors.
Among data analysts, there are also different specializations, such as financial, marketing, weather or risk analysts. Although these job descriptions have different names, they are so similar in terms of the range of tasks that a certification as a data analyst qualifies you sufficiently for these and other analyst jobs. This is not only particularly future-proof, but also makes the skills of a data analyst among the most sought-after of the 21st century.
In many areas of business and society, it is very important to actively evaluate data. Only in this way can companies gain important insights into their products, services, customers and even internal company processes and how they can be improved. In this way, they can gradually gain competitive advantages and overtake the competition. Data analysts are also in demand in socially relevant industries. The healthcare industry needs to analyze and evaluate patient data in order to obtain information about the best treatment options and develop healthcare products.
So the opportunities for Data Analysts are endless and career changers can even stay in the industry they know if they want to.

This is how much a Data Analyst earns
When it comes to choosing a suitable career, it is important to keep several factors in mind. Money alone does not make people happy, but it is without question very motivating for most employees and a material way of showing appreciation if they are also well compensated for their work. These factors are definitely present in the case of data analysts.
On average, a data analyst in German-speaking countries receives a gross annual salary of between 42,000 and 60,000 euros. As a team leader in this area, you can earn up to 90,000 euros gross per year. As is often the case, the salary varies depending on work experience, industry, specialization, particular skills, region and negotiating skills in the job interview.
Currently, several thousand data analyst positions are offered throughout Germany, on Stepstone 6971, Indeed 2.636, Glassdoor 2589 or Kimeta 3,879. With generous compensation and this wide range of unfilled positions, you no longer have to worry about your career future as a Data Analyst.
If you are serious about a career in data analysis, there are many ways to learn the skills presented in this article and become a data analyst. One of the most efficient ways to do this is through further training that prepares you for the challenges of the profession.
While many large companies are urgently trying to find and hire data experts on the job market, more and more companies are now investing in training their employees in the role of Data Analysts and Data Scientists. This is mainly because there is already a major skills shortage in this area and this is expected to increase. An additional advantage is that such employees already have invaluable experience in the industry, the market and the internals of the company.
Find out here about our Further training as a data analyst.
Sources
StackFuel (2020): "Simply Explained: What is Big Data?" [10.03.2021]
Get in IT (2021): "STARTING SALARY FOR COMPUTER SCIENTISTS 2021" [07.04.2021]
Stepstone (2021): "Data Analyst Jobs" [13.04.2021]
Indeed (2021): "Data Analyst Jobs" [13.04.2021]
Glassdoor (2021): "Data Analyst Jobs" [13.04.2021]
Kimeta (2021): "Data Analyst Jobs" [13.04.2021]





