Put simply, you can imagine a database management system (DBMS) like this: You are standing in the largest library in the world to find a specific book. You are surrounded by countless books, but they are not ordered according to any apparent structure. How are you supposed to find the book you are looking for in this mass of books, aisles and shelves? How do you find it without going through each shelf and checking each book carefully?
Most computers face a similar problem every day. This includes the transactions of your bank, the customer data in the company where you work or the location data of the warehouse from which your ordered package is shipped.
Everywhere and at all times enormous large amounts of new data produced. Without a well-defined classification system, these resemble a useless mountain of data. This is not only a waste of storage space, but also a potential for simplifying business processes, anticipating bottlenecks or acting in a more customer-centric manner.
We therefore explain below how you can bring order into your data chaos with a database management system (DBMS) and save a lot of time as well as a lot of work.
What is a database management system?
DBMS is the abbreviation for the bulky, compound word database management system. But what is a database actually? What is a database system? And what does management have to do with it? Let's start small.
Today, hardly any computer or web application works without a database system. Technological megatrends such as artificial intelligence or the Internet of Things are ensuring that we have a veritable Data flood experience. By 2025, an estimated 175 zettabytes of data will be created worldwide. By comparison, a 90-minute movie requires about 500 megabytes of storage space.
The amount of data in 2025 is equivalent to 350 trillion movies - that's a number with twelve zeros. That's a lot of zeros, isn't it? That's exactly why data needs to be structured and put into a format that is comprehensible and logical for you. But how can data be stored in a structured way and made available to you as a user in the desired form? This is where database management systems come into play.
DBMSs are part of a Database system, which consists of two core components:
- a database
- a central management interface, the DBMS
In the interaction of the two components, the database system enables you to store data in a structured way and to make it available in the desired form.
While in the Database the physical data are stored, the DBMS access to the database. Generally speaking, the DBMS is a software. It works as an interface between you as a user and the application, and takes over the task of organization and structuring. A DBMS helps you to quickly and easily gain knowledge from the stored data.
To query data from the database, there are special database languages. A well-known example is SQL (Structured Query Language). Using SQL you can store, query and manage records in the DBMS.
What are the components of a database management system?
The DBMS allows you to access the database via an interface. But only if you have the appropriate Access rights you can make database queries or use the data for other applications. Database management systems thus make an important contribution to Security and data protection in your company.
In order to store data in a structured way and make it retrievable, the systems consist of various components. The main components are:
- the Data definition language
- the Data manipulation language
- the Data dictionary
The Data definition languagealso called Data Definition Language (DDL), defines the actual structure of the database. You can create, modify or delete individual objects such as references, relationships or user rights using the definition language.
With the help of the Data manipulation languageData Manipulation Language (DML) is used to edit the actual data. In this way you can delete, insert, modify or read out records.
The Data dictionary has the task of providing all information about the data stored in the database. This metadata, or "data about data", tells you about the contents of the various data in the data store.
What are the database management system models?
The way the DBMS structures and manages data depends on the database model. There are a variety of database models, which are characterized by different properties.
The most widespread is the relational database model. Here you organize data in the form of tables. Each row forms a so-called Entityfor example, a movie. Each entity has certain attributes that you can read in the table columns. In a movie database, each movie has a number of different attributes, such as title, genre, or a length. The advantage of relational databases is that a wide variety of different Relationships between the data can be mapped and represented by values in table columns.
It is important that you clearly distinguish the individual entities. To do this, you assign a so-called unique primary key to each line. In our example, this is a movie ID that was generated automatically.
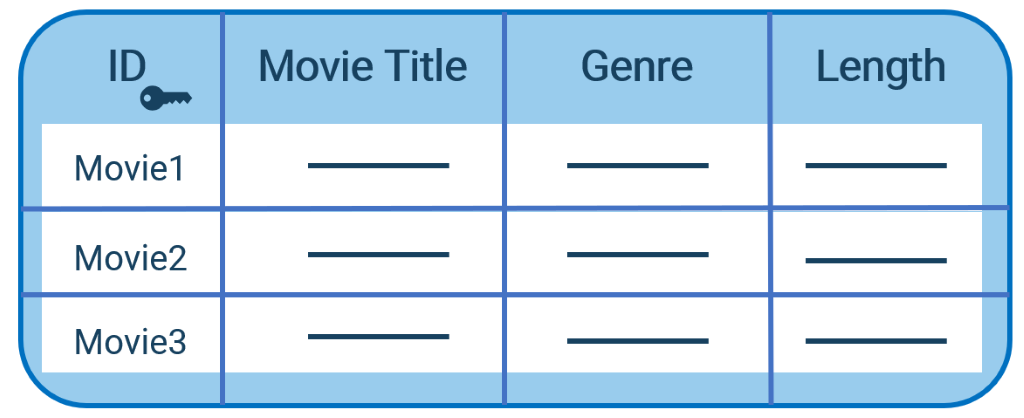
Figure 1: Data storage in the relational database model
The procedure is different for a hierarchical database model. Here are the data in a kind of Parent-child relationship to each other. This model is represented with a hierarchical tree structure, which allows you a quick read access. The top hierarchical level, the so-called root of the tree, represents the entire film collection. In the individual leaves of the tree you will find the films and the attributes of the individual films.
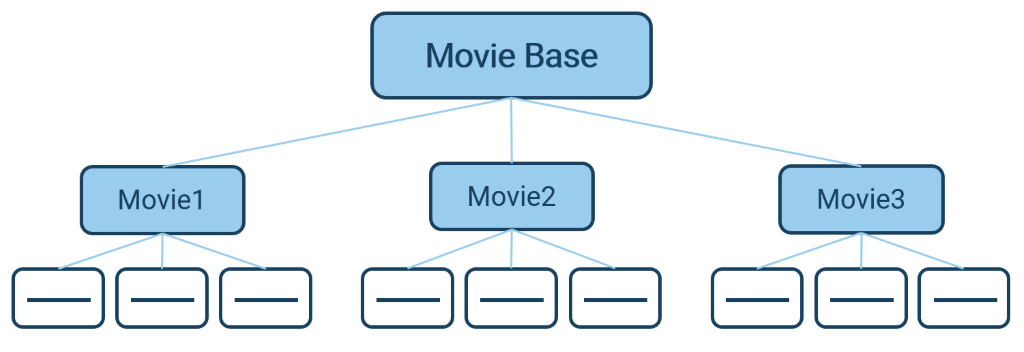
Figure 2: Data storage in the hierarchical database model
Relational or hierarchical database models store structured data. But what happens when you want to manage unstructured data like images or audio files? This data and information cannot be stored in the form of tables. For this case so called NoSQL databases developed. Here you organize the data in the form of Key-Value-Pairs (Key-Value-Pairs).
What are the advantages of database management systems?
As the cornerstone of database systems, database management systems offer many advantages. Without the DBMS you would not be able to manage, control or monitor your database. In particular, it facilitates the management of large data sets. Through the structuring you can easily and quickly access stored data. Besides a high flexibility, the database management system also regulates the access of the users and can support you and your company in data protection.
Let's go back to the example from the beginning: the confusing library. Wouldn't it be helpful if the books were also sorted according to a certain system? For example, we could assign a unique Book ID to the books and then sort them in ascending order on the shelves. Now, when you are looking for a particular book, you know exactly on which shelf and at which level you will find it.
As we all know, order is half the battle. Do you want to tidy up your database? Then we have the right resources for you. We are happy to help you and support your company in drawing the right conclusions from valuable company data quickly and easily. Book a non-binding expert call now.
Sources
Wikipedia (2022): "Key values database" [14.10.2022]





