Digitization is happening. In all areas and everywhere.
Increased customer satisfaction, more revenue through new business models, more efficient work in the digital workplace, more flexibility with the cloud are just a few of the many reasons why digitization brings added value to the company. This can be enabled mainly by shortening work processes and fast data collection. To achieve digitization, companies not only need to invest money in modern technologies, but also be open to the new possibilities, retrain employees and prepare for the VUCA-Set environment.
The most frequently required skills in the next few years are strongly related to dealing with digital transformation. At the top of the list are the skills of data analysis and the complex handling of big data. 42 percent of the almost 500 marketing professionals surveyed in November 2020 see this as particularly relevant for the future.1

Complex data analysis is not only important for IT departments, but should be implemented in research & development, sales, marketing and HR management. This applies across all industries. It is also relevant for areas that have previously been less digitally influenced. Expertise in complex data analysis is therefore becoming a central interface competence in companies.
Skill gaps are seen in the area of UX design, but also in general expertise with IT software. Collaborative cooperation within the company's departments is necessary in order to exploit potential and promote additional skills. A modern organization practices New Leadership. This also includes leading virtual teams in the home office and the practical application of design thinking to promote innovation and creativity.2 The basic prerequisite for a digital mindset is a general openness to new processes, but also to other learning cultures. In order to be able to learn from each other as well, constructive engagement with other perspectives is necessary. Digital trends, such as artificial intelligence, can thus be recognized and used.
The labor market's need for digital skills has risen sharply in recent years. In Germany alone, there is a need for 700,000 workers to have digital skills by 2025.3 Digital skills are not just technical or specialist skills; soft skills and the general ability to get involved with new things are also essential. Further development of their own digital skills is important for 40-50 percent of the workforce in Germany.4 Isolated training courses are not enough to close the skills gap.5 Companies need an innovative approach.
Digital technologies determine everyday life and many occupational fields. Especially in the manufacturing sector, digital skills are necessary to be ready for the demands of the future on the labor market. Based on an online survey in June 2018 of more than 600 companies in Germany, there will be a need for around 700,000 additional workers with digital technology skills over the next five years.6 According to a study by Bitkom Research, around 86,000 experts are currently being sought for IT and data analysis in 2020.7
Every second worker needs to acquire additional skills to keep up with the new demands on the labor market.8 Many people think of programming skills or robotics, but that's just the tip of the iceberg. Digital skills are not just technical knowledge. Soft skills are essential for successfully addressing the requirements of digitization.
The management and strategy consultancy McKinsey has developed a future skills framework in collaboration with the Stifterverband and various companies. This framework maps the current and future skills requirements of the German economy and society. Future skills are defined as "competencies that will become significantly more important in the next five years for [professional] life or participation in society."9
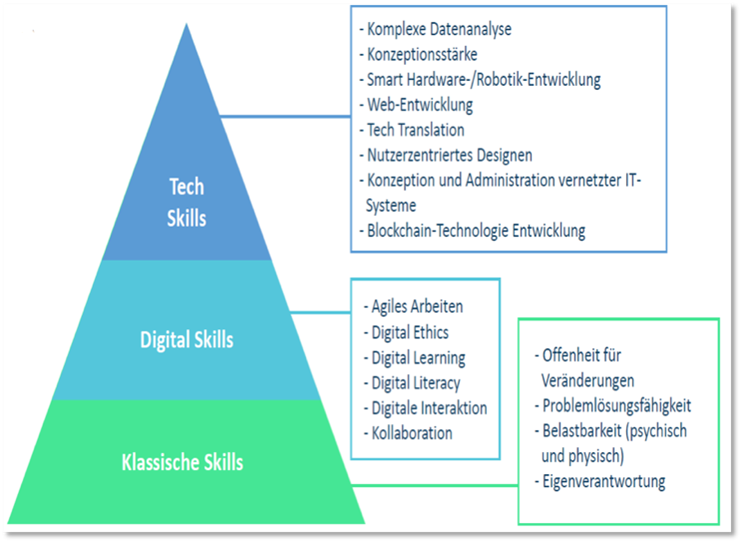
Source: Framework adapted from Stifterverband, McKinsey (2019).
Technological skills are essential for the implementation of new technology. Cloud computing, UX design or even AI programming require special expertise. In order to be able to find one's way in the digital world at all, certain basic skills are necessary. These are assigned to the second level of the framework, while the third level includes classic skills and competencies such as stamina, creativity and adaptability. These make it significantly easier to find one's way in complex situations. Such competencies form the basic framework and can then be linked to technological skills. For companies, the challenge lies primarily in the selection of qualified specialists. Tomorrow's employees should have a skillset that enables them to integrate traditional and digital competencies in their day-to-day work. 10
New technologies have a significant impact on the labor market. It is often assumed that digitization will destroy jobs. But the opposite is the case. Digitization already created 1.5 million new jobs in 2012 alone. According to the World Economic Forum's Future of Jobs Report 2020, jobs with special IT skills such as software developer or data analyst will be more in demand than ever in the coming years.11
According to a projection, more than 2.4 million workers in Germany need to be trained in key skills such as agile working or digital learning.12 The comparison between the people who already have the individual skills today and those who would have to have them in five years from the company's perspective shows a high need for further training. Implementing the hot skills of the future requires learning with a meaningful strategy. Above all, the practical application of the newly learned content is important to make continuing education successful. At Stackfuel, re- or up-skilling consists of 8 percent theoretical text content, 12 percent tutorials in video format, 45 percent practical business cases and 35 percent coding challenges. This means that the learning content and the use of new technologies can be experienced and applied directly in one's own work context.
For an individual learning experience in the area of digital skills, Peers offers learning paths differentiated by industries, disciplines and skills. It builds on the McKinsey framework and uses a learning architecture that combines theory and practice.

For companies, the challenge lies primarily in the selection of qualified specialists. Isolated training courses are not enough to close the skills gap.13 50 percent of all people will need reskilling by 2025.14 Stackfuel sees the potential in all employees to become experts in digital skills. Coding challenges are also used to apply the new knowledge directly. In this way, individual training takes place from beginner to professional, adapted to the individual level. Through mentoring, Stackfuel accompanies the entire process of upskilling and thus makes the company fit for the requirements of the future.
With Peers, training is aligned with the company with the help of an AI. After a needs analysis with the management, the learning paths are adapted to the level of competence of the employees. The best and most suitable trainings, e-learnings, coachings, etc. are selected and organized on the digital learning platform. With renowned partners, such as Stackfuel, this ensures that further training leads to better work results.
Bibliography
- Lashbrook, J. (2020). What Are the Most Desirable Digital Marketing Skills Heading into the New Year? Marketing Charts. https://www.marketingcharts.com/business-of-marketing/staffing-115467
- Lashbrook, J. (2020). What Are the Most Desirable Digital Marketing Skills Heading into the New Year? Marketing Charts. https://www.marketingcharts.com/business-of-marketing/staffing-115467
- Stifterverband für die Deutsche Wissenschaft e.V.: Kirchherr, J., Klier, J., Lehmann-Brauns, C. & Winde, M. (2018.) Future Skills: What skills are missing in Germany. Future Skills Discussion Paper, 1. Essen. S. 10.
- Schallenberg-Kappius, J. (2021). Reskilling - This founder wants to move people from analog to digital jobs.
- Accenture (ed.): Donald B. Vanthournout (2006): Return on learning, Part 1: Generating business impact from an enterprise learning transformation program; p.6.
- Kirchherr, J.; Klier, J.; Lehmann-Brauns, C.; Winde, M.; p. 2.
- Bitkom e.V. (2020). 86,000 vacancies for IT specialists. https://www.bitkom.org/Presse/Presseinformation/86000-offene-Stellen-fuer-IT-Fachkraefte
- Schallenberg-Kappius, J. (2021). Reskilling - This founder wants to move people from analog to digital jobs.
- Kirchherr, J.; Klier, J.; Lehmann-Brauns, C.; Winde, M.; p. 2f.
- Kirchherr, J.; Klier, J.; Lehmann-Brauns, C.; Winde, M.; p. 10.
- World Economic Forum (ed.) (2020). The Future of Jobs Report. Cologne/Geneva. http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Future_of_Jobs_2020.pdf. P. 29f.
- Kirchherr, J.; Klier, J.; Lehmann-Brauns, C.; Winde, M.; p. 10.
- Kirchherr, J.; Klier, J.; Lehmann-Brauns, C.; Winde, M.; p. 10f.
- Schallenberg-Kappius, J. (2021). Reskilling - This founder wants to move people from analog to digital jobs.



